Where science
meets heart
PK Deficiency Resources
for Healthcare Providers
Clinical trials
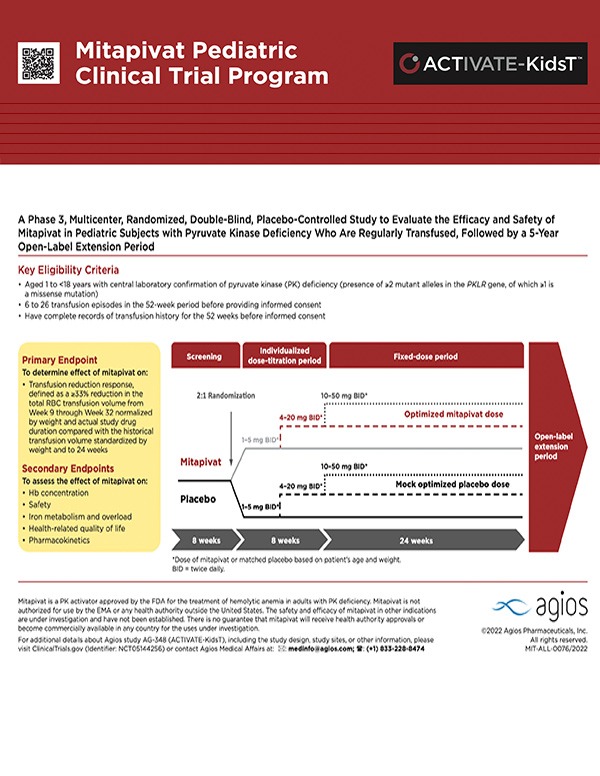
Pediatric PK Deficiency Clinical Program
Agios is committed to developing innovative treatment options that make a meaningful difference in patients’ lives and fundamentally change the way rare and genetically defined diseases are treated. We are leveraging our leadership in PK activation to explore an investigational, oral treatment for pediatric PK deficiency. More information about our active trials is below.
Peak Registry
Due to the rarity of PK deficiency, its prevalence, clinical burden, and long-term clinical course are not well defined. Peak is an ongoing, longitudinal, observational registry study designed to address this gap. Its primary objective is to record the natural history, treatment, outcomes, variability in clinical manifestations and disease burden of patients with PK deficiency. Approximately 500 patients are targeted for enrollment over 7 years at an estimated 60 study centers in up to 20 countries. Site and patient recruitment began in 2018 and all enrolled patients will be followed prospectively for at least 2 years (up to 9 years).
Patient experience
PK Deficiency White Paper
The white paper, entitled “PK Deficiency: Reflections on the Patient Experience to Support Treatment and Care,” shares the results of an international survey designed to explore communication between PK deficiency patients and caregivers and their hematologists. It explores in detail how the survey findings can inform approaches to improve PK deficiency disease management and patient experience. Given PK deficiency prevalence, the survey is thought to be the largest of its kind for the PK deficiency community to date.
The survey and white paper were developed by the PK Deficiency Advocacy Advisory Council (AAC), an international, multi-disciplinary group of experts, including patients, caregivers, patient advocates and clinicians, including representatives from the Thalassaemia International Federation (TIF), Metabolic Support UK, the National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD), Thrive with Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency and the Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency Foundation. The vision of the AAC is that people around the world affected by PK deficiency receive timely diagnosis and can easily access the education, support and care they individually need. All AAC activities, including the survey and white paper, are funded by Agios.
“Just Listen: Voices of PK Deficiency” Podcast
Just Listen: Voices of PK Deficiency is a podcast about pyruvate kinase (PK) deficiency and is intended for patients, caregivers, providers and the greater community of people who are impacted by PK deficiency. Each episode strives to provide listeners with critical education, the latest scientific updates and voices from the PK deficiency community. The podcast is sponsored by Agios Pharmaceuticals, Inc. The program is intended for informational and educational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. Host and guests featured in each episode have been compensated for their time.
Scientific resources
Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease (SCD), a monogenetic disease of hemoglobin, affects millions across the globe. The resulting sickled red blood cell (RBC) leads to a host of complications including anemia, hemolysis, and episodes of acute pain, among others. People with SCD continue to have needs not met by current therapies. At Agios, we are studying how PK activation could potentially benefit people with SCD. PK activation reduces 2,3-diphosphoglycerate (2,3-DPG) levels in RBCs which increases hemoglobin oxygen affinity, reducing hemoglobin S polymerization and may inhibit the sickling process. At the same time, increasing adenosine triphosphate (ATP) enhances the energy metabolism of the RBC which may lead to improved membrane integrity and RBC health. Currently, Agios is studying PK activation in adults with SCD in ongoing clinical trials to assess both the effect on anemia and vaso-occlusive events.
Thalassemia
Thalassemia is a diverse group of genetic disorders with a worldwide distribution that are characterized by reduced or absent production of hemoglobin. Imbalanced globin chain production that occurs in thalassemic red blood cells leads to ineffective erythropoiesis, hemolysis, and dysregulated iron homeostasis, resulting in the development of anemia and other clinical complications. Although important advancements in the management of thalassemia have been made over the last few decades, significant unmet needs remain that are not addressed by current approaches. Agios is studying how PK activation could potentially benefit people across the full range of thalassemia types, including both α- and β-thalassemia. PK activation increases adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and enhances the energy metabolism of the red blood cell (RBC), which may lead to improved membrane integrity and RBC health. Currently, Agios is studying PK activation in adults with non-transfusion-dependent and transfusion-dependent thalassemia in ongoing clinical trials to assess effects on both anemia and transfusion burden.
For medical information queries, please contact us at the phone numbers or email addresses below.
Report an adverse event or product complaint anytime.
Outside the U.S.:
All countries: ex-usmedinfo@agios.com
France: +33 801841438
Germany: 08001090777
Italy: +39 800596326
Spain: +34 900990230
Monday – Friday
9:00 am – 5:00 pm Local standard time
This site is intended for healthcare professionals; all materials available are for scientific informational purposes only.
Resources available may include educational and information materials relating to Agios’ clinical pipeline, investigational products, therapeutic areas of interest, approved medicines, congress materials, and publications. This site may include information that has not been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. There is no guarantee that investigational products will receive health authority approvals or become commercially available in any country for the uses under investigation. For approved product full prescribing information, including indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions, and adverse events, please refer to approved product labeling.
MIT-ALL-0179 11/22